Researchers Zhengyi Luo and colleagues from the College of Civil Engineering, Hunan University in China, have introduced an innovative approach to managing smart home energy systems. The study, published in Advances in Applied Energy, presents a user-friendly and adaptive home intelligent agent with self-learning capabilities designed for the optimal scheduling of smart home energy systems. With its intuitive design, the technology marks a significant advancement in home energy management, promising to enhance system performance while being practical for everyday use.
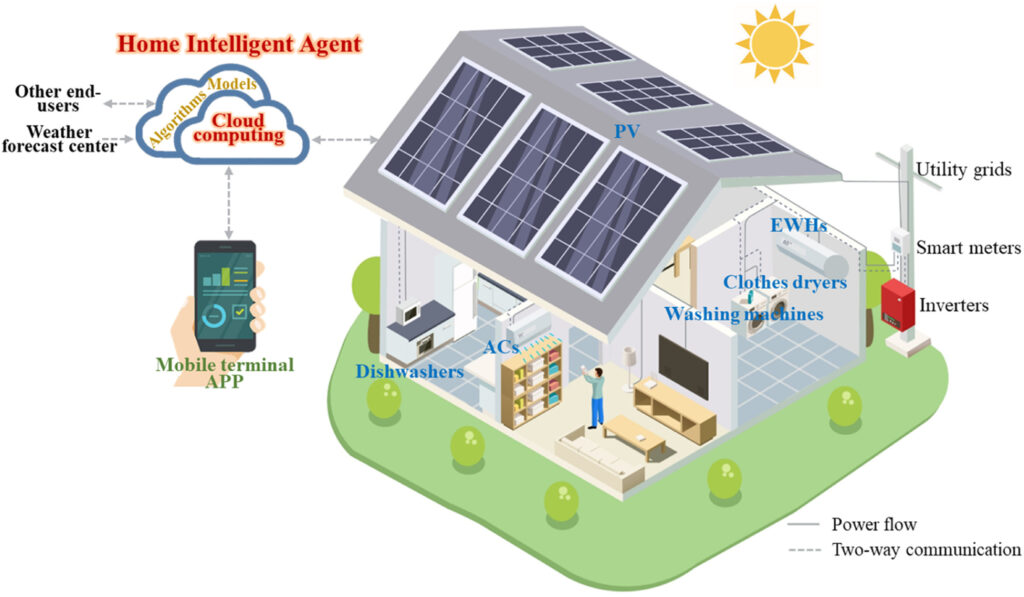
Diagram of the Home Intelligent Agent managing various smart home devices from the article.
The intelligent agent autonomously identifies model parameters based on system operation data, eliminating the need for manual input and making it more practical for everyday use. This capability allows the agent to self-learn the latest energy consumption information from updated datasets and adaptively adjust model parameters to accommodate changing conditions. This adaptability ensures that the model remains accurate and effective over time, providing a reliable solution for long-term energy management.
The intelligent agent can significantly enhance system performances by reducing operational costs, peak-valley differences, and CO2 emissions while improving self-consumption and self-sufficiency rates,” the researchers explained. Experimental studies conducted on a laboratory-based smart home energy system verified the effectiveness of this intelligent agent across different scenarios. The results consistently showed that the agent’s accuracy was high, with errors below -12.7%. By scheduling optimally, the system performances were significantly improved, leading to a substantial reduction in daily operational costs by 34.1% to 81.6%. This has instilled confidence in the technology’s benefits by providing financial security.
This research addresses several critical challenges in deploying Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS) in real-world environments. Traditional HEMS often require users to manually input numerous model parameters, which can be cumbersome and lead to inaccuracies. In contrast, the proposed intelligent agent automatically identifies these parameters, making the system more user-friendly and reducing potential errors. Additionally, the intelligent agent’s ability to self-learn and adapt to changing conditions ensures that it remains effective even as external factors evolve.
The practical implications of this technology are vast. The intelligent agent can significantly reduce electricity bills and enhance energy consumption efficiency by enabling optimal scheduling of smart home energy systems. This is particularly important as the adoption of renewable energy sources like photovoltaic (PV) generation increases. Dr. Luo explains, “Leveraging residential load flexibility can mitigate the impacts of PV generation on utility grids, associated with reducing the required capacity of battery storages and enhancing system resilience.”
One of the standout features of the intelligent agent is its consideration of the benefits of diverse stakeholders, including end-users, grid operators, and policymakers. By balancing the interests of these different groups, the agent ensures optimal scheduling benefits individual households and supports broader energy management goals. This holistic approach is crucial for widespread adoption of smart home energy systems.
The study’s experimental validation proves the intelligent agent’s effectiveness. The experiments were conducted in a controlled laboratory environment at Hunan University, China, using a smart home energy system with distributed PV generation and flexible and non-flexible loads. The intelligent agent managed the system’s operation, performing day-ahead optimal scheduling and automatically controlling the system based on the obtained operation schemes.
In one scenario, the intelligent agent optimized the operation of air conditioners, electric water heaters, washing machines, and dishwashers, shifting their usage to times when PV generation was sufficient. This reduced reliance on grid electricity and maximized the use of renewable energy, demonstrating the agent’s potential for enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability.
In conclusion, developing this intelligent agent significantly advances smart home energy management. Its user-friendly design, self-learning capability, and adaptability make it a practical and effective solution for optimizing household energy use. Dr. Luo notes, “Our intelligent agent provides invaluable guidance for the optimal dispatch of smart home energy systems in real-world settings, paving the way for more efficient and sustainable energy consumption.”